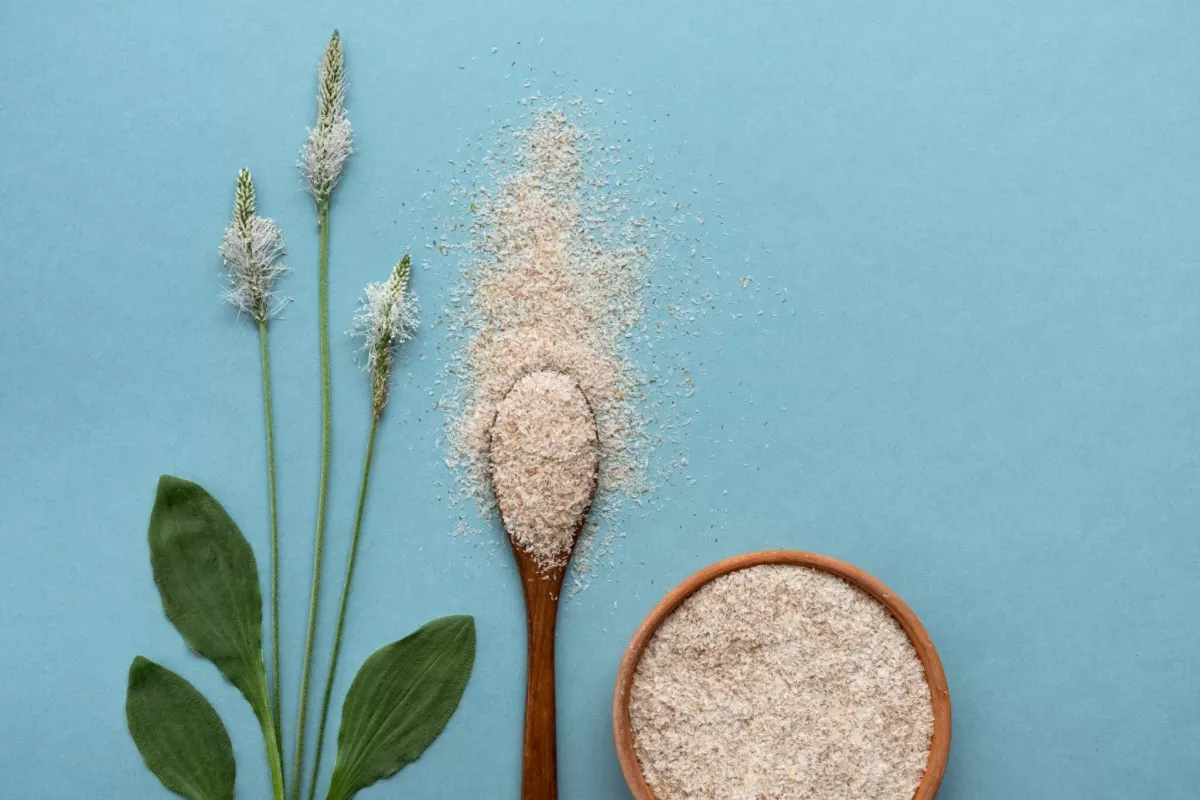
Your intestines grumble, pinch and cause you pain? A proven home remedy for digestive problems are psyllium husks. Learn in our article, for what psyllium husks are good: How the small seeds work against diarrhea and constipation and why they are good for a healthy digestion.
What is in the seeds
Apart from their appearance, psyllium seeds have nothing in common with fleas. They are seeds of plantain plants, which have been used for centuries as a medicinal plant for gastrointestinal complaints. In naturopathy, the seeds are also used as a natural remedy for intestinal cleansing.
Psyllium and psyllium husks consist largely of dietary fiber. These are fibrous plant substances which are beneficial for our digestion and satiety. The dietary fibers from psyllium seeds are multiple sugars of xylose, arabinose and galacturonic acid. They act as mucilage in the human body and this is something desirable because mucilage has a beneficial effect on the intestines and increases stool volume. You can think of these mucilages as a nourishing cream for your intestinal wall.
In addition, psyllium husks also contain vegetable oils, which act like a lubricant to ensure that the intestinal contents are transported further, and small amounts of proteins.
The effect of psyllium husks – what are they good for?
In the stomach and intestines, the fiber substances from the psyllium husks swell up. Only a small part of these substances can be metabolized by intestinal bacteria. Instead, the seeds form a kind of gel that helps to transport the contents of the intestine. The seeds bind large amounts of water to themselves. This leads to an increased stool volume and at the same time the intestinal movement is stimulated in this way.
Psyllium husks and the gastrointestinal tract
- Constipation & psyllium husks: Mucilage makes the stool more slippery, thus the intestinal contents move forward by intestinal activity. In addition, the increased stool volume pushes more forward. All these effects make going to the toilet easier. Psyllium is thus a real helper in cases of constipation. In a scientific study, researchers also found that the effect of psyllium husks influences the intestinal flora. The composition changes for the better. This could also have an influence on digestive complaints.
- Diarrhea & Psyllium Seeds: The seeds contain valuable soluble fiber, these absorb the excess water in the intestine and thus change the consistency of the stool. In short, the effect of the seeds is that the stool becomes firmer.
Psyllium husks for general health
- Cholesterol-lowering property: Dietary fiber binds bile acid in the intestine, which contains cholesterol. In this way, the body can excrete cholesterol, which may be reflected in the cholesterol level.
- Stabilize blood sugar levels: Psyllium husks cause the sugar from food to be absorbed more slowly and blood sugar fluctuations are weaker. This leads to stable blood sugar levels and can help prevent type 2 diabetes.
- Lose weight: Dietary fiber satiates well and facilitates weight loss. You can read more about this topic here: How a high-fiber diet helps you lose weight.
- Losing weight with gastric balloon: Especially after an intragastric balloon has been implanted, psyllium husks can be helpful. The body must first get used to its new roommate and the new conditions. If a patient experiences digestive problems during this time, psyllium husks can have a balancing effect on the intestines. If you suffer from diarrhea or constipation during the gastric balloon therapy, discuss this with your Weight Buddy. Together you will find a quick way to get better.
- Intestinal diseases and hemorrhoids: Psyllium is also used for hemorrhoids, because the mucilage makes stool easier to settle.
Psyllium, psyllium husk, Indian psyllium husk & ground psyllium husk – what are the differences?
On the market there are a variety of products with psyllium and psyllium husks. But what are the differences and which products are useful?
- Psyllium seeds are the whole seeds of the plantain family Plantago psyllium (shrub plantain), Plantago indica (sand plantain) or Plantago ovata (Indian psyllium). Compared to psyllium husks, they have less fiber and a lower swelling capacity, but they have more protein and they are more natural because they are less processed. Because psyllium seeds form lower amounts of mucilage, they are more comfortable for some people to use, but they also have less effect. Psyllium seeds are thus a good remedy for healthy digestion when there are no medical conditions. They can be incorporated into the daily diet, for example in muesli.
- Psyllium husks are, as the name suggests, the shells of psyllium seeds. The hulls contain more fiber than the whole seeds and therefore have a greater effect on the intestines. In cases of diarrhea or constipation, using the hulls instead of the whole psyllium seeds is recommended because of the greater effect.
- Indian psyllium husks: From India or Pakistan come almost all psyllium seeds that are available in our country. Indian psyllium husks come from a certain plantain called Plantago indica. Whether these seeds are better or worse than other psyllium husks cannot be said.
- Ground psyllium husks: Most psyllium husks are ground. They come in fine and coarse. The difference is in the consistency. Some people find finely ground psyllium husks more pleasant to take. However, the effect is the same.
What you should know about taking psyllium husks
Whether psyllium or psyllium husks, both require water to swell. About 200 ml of water per dose are necessary to the usual drinking quantity. This also means that you must not include the liquid that the psyllium seeds require in your drinking quantity. The water must therefore be drunk in addition. Attention: if you do not drink enough, constipation can even lead to intestinal obstruction. Sufficient liquid is therefore the be-all and end-all when taking psyllium.
Even though medicinal plants and dietary supplements are not drugs, they can cause side effects or interactions with medications. For example, psyllium can slow the absorption of vitamins, cardiac glycosides and blood thinners. Thyroid hormones may also be affected. A time interval of at least 30 to 60 minutes should therefore be observed.
Since psyllium and psyllium husks can bind an extremely large amount of liquid, too much is rather harmful. You should use a maximum of 40 grams of psyllium powder per day. This amount must then be divided into several portions. When you start taking psyllium, 40 grams is too much for you. Start with 10 grams and increase the dosage slowly, otherwise you may experience bloated belly and unpleasant intestinal sounds.
You should also get moving after using psyllium. Laying on the sofa or lying down to sleep immediately after ingestion is unfavorable, because the husks can then bind lumps in the esophagus. Light movement after ingestion prevents this.
Recipes with psyllium husk for your everyday life
- Classically with water or juice: Stir 10 grams of psyllium husks into 200 ml of liquid. Allow to swell for 10-20 minutes and drink.Tip for gastric balloon patients: Take small sips throughout the morning. You may only use psyllium seeds if you have been drinking at least 1.5 liters of liquid so far.
- Porridge with psyllium husks: Swell 150 ml of milk or vegetable drink with 35 g of oat flakes, 1 tsp of flaxseed and 1-2 tsp of psyllium husks overnight in the refrigerator. Enjoy the next day with fruit of your choice.
- Psyllium pudding: 0.5 tbsp psyllium husks, 0.5 banana, 20 g cashews, 2 dates without stone, puree with 200 ml water. Season the mixture with cinnamon or cocoa and leave to swell in the refrigerator for 10-20 minutes. Serve with fruit if desired.
Sources:
Granitzer E, Meier B, Drexel H, Saely CH. [Auswirkungen von Flohsamen (Psyllium) auf Parameter des Glukosestoffwechsels: Eine Übersicht]. Complement Med Res. 2017;24(3):164-171. German. doi: 10.1159/000477366. Epub 2017 Jun 8. PMID: 28586775. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28586775/
Jalanka, J., Major, G., Murray, K., Singh, G., Nowak, A., Kurtz, C., Silos-Santiago, I., Johnston, J. M., de Vos, W. M., & Spiller, R. (2019). The Effect of Psyllium Husk on Intestinal Microbiota in Constipated Patients and Healthy Controls. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(2), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020433

The yo-yo effect, ravenous appetite, stress - losing weight can be quite frustrating. But there is a way out for everyone. Together we will find the right solution for you. As a nutritionist at My Weight®, I support my patients individually and personally on their way to their desired weight. Losing weight can and should be fun...and we work on that together!
Maren - Weight Buddy® and Nutritionist at My Weight®

 English
English  Nederlands
Nederlands  Deutsch
Deutsch 


